updated November, 2025
Why Social Emotional IEP Goals Matter
In today’s classrooms, social emotional learning (SEL) is just as important as academics. For students with exceptionalities, social emotional IEP goals help build confidence, improve self-regulation, and support healthy relationships. These goals give students the tools to navigate challenges, express feelings appropriately, and connect with others.
Special education teachers know: emotional growth leads to academic growth. Setting clear, measurable SEL goals helps both.
How to Write SMART Social Emotional IEP Goalsa
When writing any IEP goal, use the SMART framework:
- Specific — Define the exact skill.
- Measurable — Set a way to track progress.
- Achievable — Match the student’s current ability.
- Relevant — Connect to the student’s real needs.
- Time-Bound — Include a deadline or mastery period.
20 Social Emotional IEP Goals (With Examples)
Below are 20 teacher-tested examples that you can individualize for your students.
1. Identifying Emotions
The student will identify their feelings using visuals or words in 4 of 5 opportunities as measured by teacher data.
2. Expressing Emotions Appropriately
The student will use appropriate words or actions to express feelings 80% of the time.
3. Using Coping Strategies
When upset, the student will choose a self-calming strategy (deep breathing, counting, or break card) in 4 of 5 trials.
4. Managing Frustration
When given a difficult task, the student will verbalize frustration instead of refusing or leaving the area in 3 of 4 trials.
5. Improving Self-Regulation
Using a feelings chart, the student will identify and adjust emotional state within 5 minutes of teacher cue, 80% of the time.
6. Demonstrating Self-Control
During group work, the student will stay on task and follow rules for 10 consecutive minutes in 4 of 5 sessions.
7. Increasing Self-Awareness
The student will describe strengths, triggers, and growth areas using a reflection journal in 4 of 5 opportunities.
8. Goal Setting
The student will set one personal or academic goal, monitor progress weekly, and reflect on growth during check-ins.
9. Building Empathy
The student will recognize peers’ emotions and respond appropriately in 3 of 4 observed interactions.
10. Positive Peer Interactions
The student will share, take turns, and use kind words in 80% of social opportunities.
11. Following Directions
After a two-step direction, the student will comply without argument in 4 of 5 opportunities.
12. Accepting Feedback
When corrected, the student will respond appropriately and without avoidance in 4 of 5 opportunities.
13. Problem-Solving Skills
When faced with a conflict, the student will identify the problem and two possible solutions in 3 of 4 situations.
14. Conflict Resolution
The student will use calm communication or “I-statements” to solve disagreements in 4 of 5 opportunities.
15. Seeking Help
When frustrated, the student will request help from an adult instead of avoiding the task in 4 of 5 instances.
16. Resilience and Perseverance
The student will attempt to complete challenging tasks for at least five minutes before asking for assistance.
17. Self-Advocacy
The student will appropriately express personal needs (e.g., “I need a break”) in 80% of opportunities.
18. Recognizing Boundaries
The student will respect personal space and property in 4 of 5 settings.
19. Responsibility and Accountability
The student will complete assigned tasks and take ownership of choices in 4 of 5 trials.
20. Positive Self-Talk
The student will use positive affirmations or coping statements when challenged in 80% of opportunities.
Tips for Tracking SEL Progress
- Use daily behavior charts or check-ins.
- Track progress with teacher and student reflections.
- Collect data across multiple environments.
- Incorporate visual aids and progress scales to promote independence.
Free Resources for Teachers
💡 Try These SEL Tools:
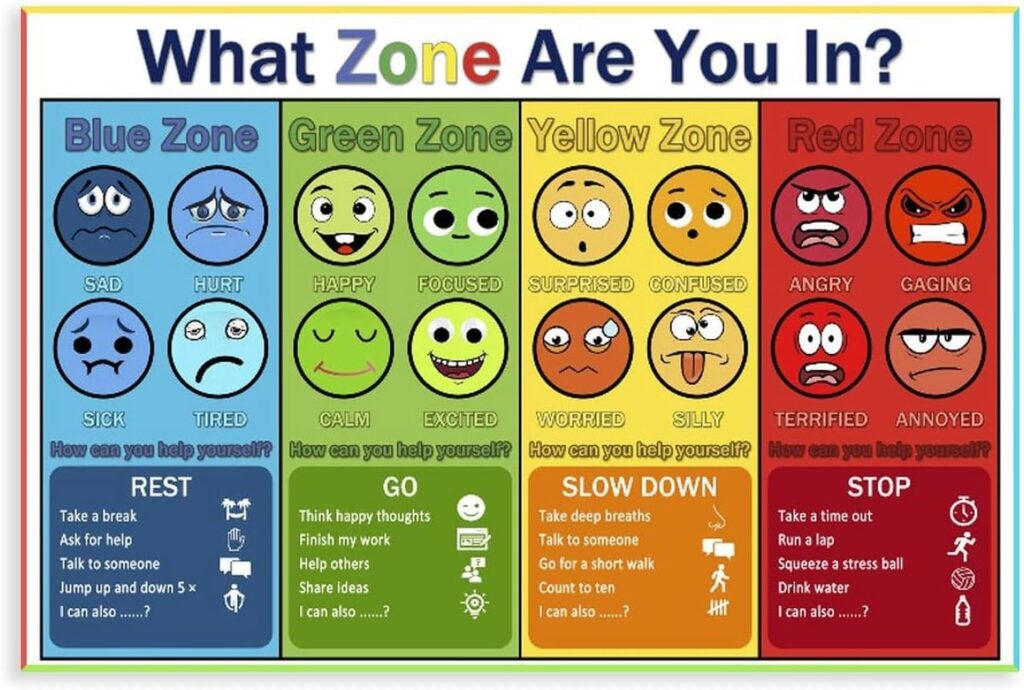
- Zones of Regulation posters
- Feelings check-in chart
- Behavior reflection journal
- Goal-tracking sheets
- Calm corner visuals
👉Do you need an Advocate? Find out!
Final Thoughts
Social emotional IEP goals don’t just improve behavior—they shape confident, compassionate learners. By setting clear expectations, tracking growth, and celebrating small wins, teachers can help students thrive socially and emotionally in every setting.
Check out The Essential Skills Every Child Needs to Develop: 6 Foundations for Growth and Success